Why Docker on a Linux Container?
Simply put – saving resources. Proxmox official support would always recommend that you run Docker in VMs, but the disadvantage to that is that VMs require more resources from the hypervisor. Running Docker in a Linux Container (LXC) will allow you to run Docker at a fraction of the resource requirements with much faster boot speeds.
ℹ️
Any time you want to run Docker on a Linux Container, simply repeat the steps as documented here.
✔️
Using ZFS?
These steps were tested on a Proxmox node configured with ZFS and no observable issues could be detected.
These steps were tested on a Proxmox node configured with ZFS and no observable issues could be detected.
Preparing Proxmox
Ensure FUSE OverlayFS is Installed on the Hypervisor
ℹ️
fuse-overlayfs is really only required if your Proxmox node's storage backend is ZFS, as my research indicates that this is a requirement for keeping Docker volume sizes from blowing upapt clean && apt update
apt install -y fuse-overlayfsCreate a Linux Container and Test Functionality
Create the Linux Container
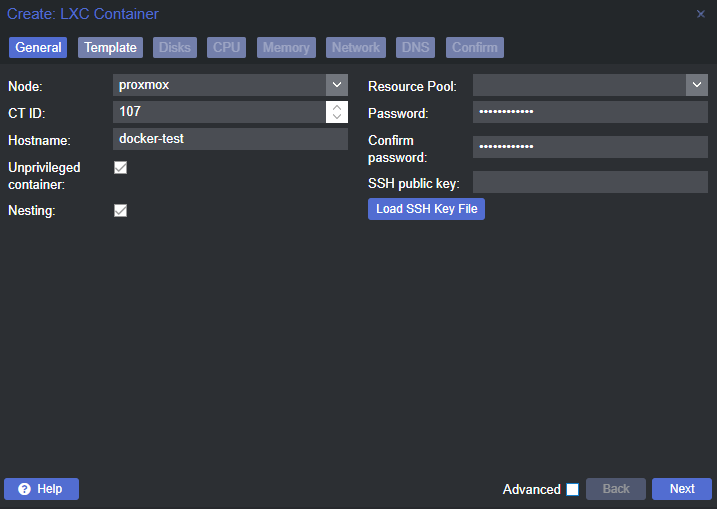
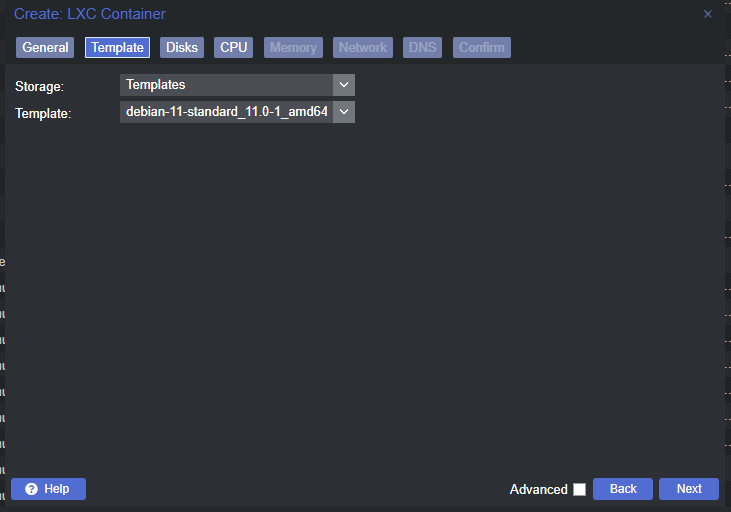
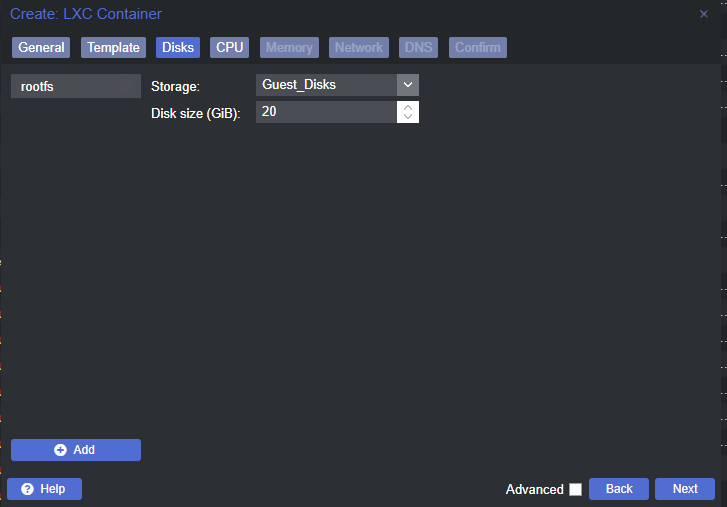
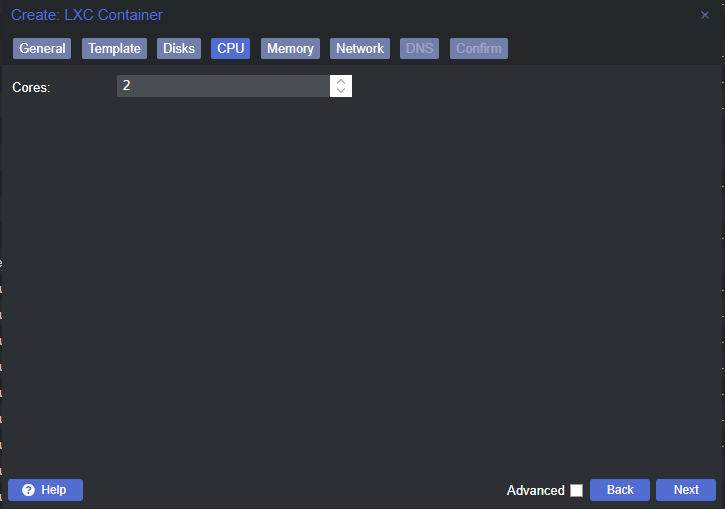
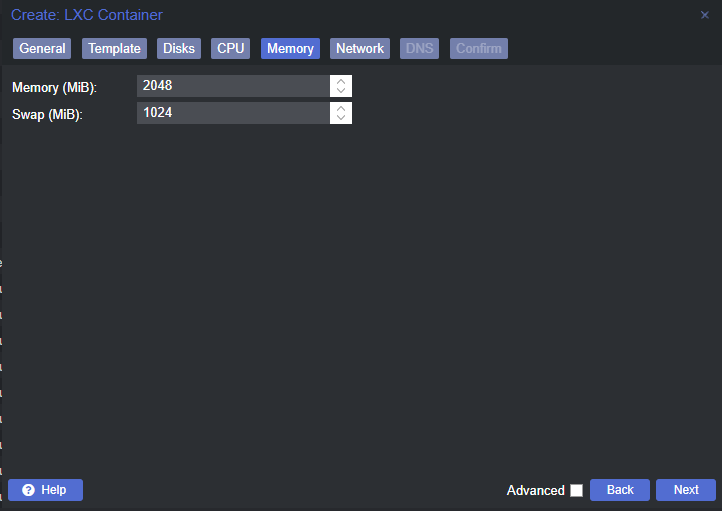
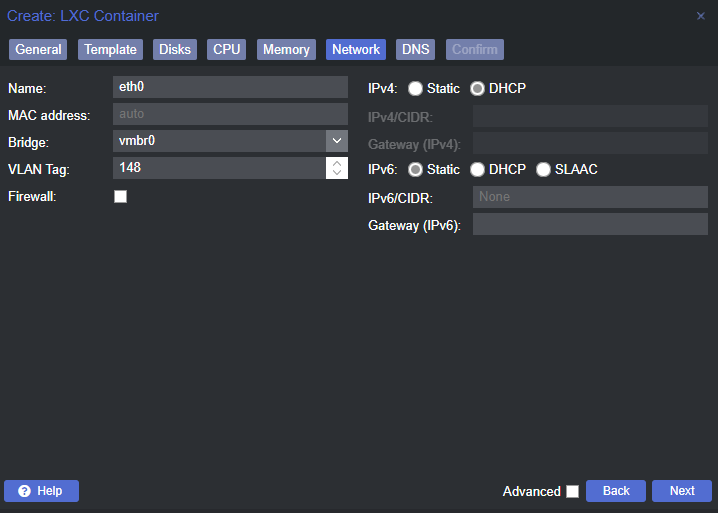
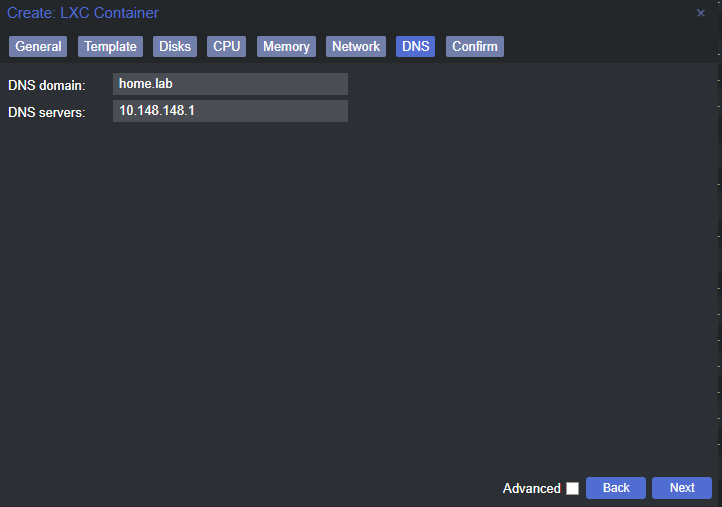
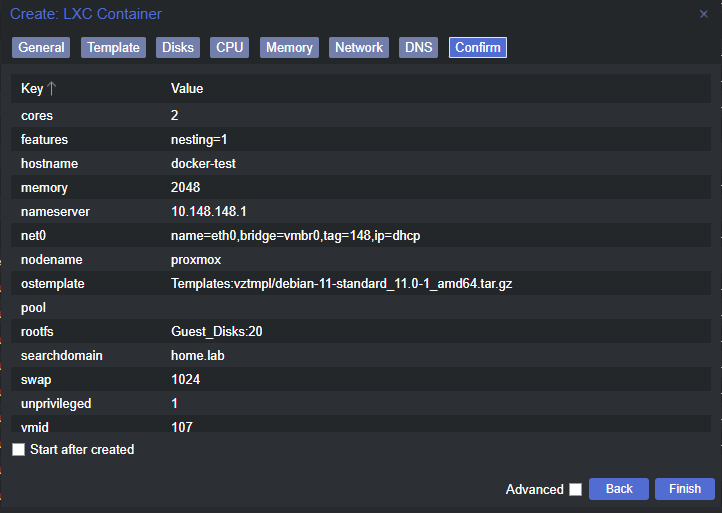
Change a Few Container Options
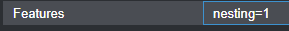
ℹ️
As mentioned earlier, you only need to enable
FUSE if your Proxmox storage backend is ZFS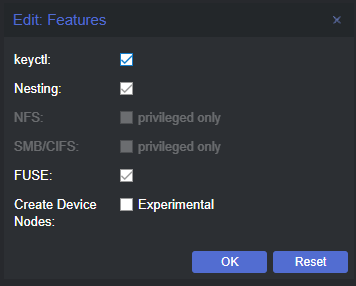
You may now start the container.
Configure and Test Docker
Install and Configure FUSE OverlayFS on the Linux Container
ℹ️
Repeating here, once again, that you only require
fuse-overlayfs if your Proxmox node storage backend if ZFSapt clean && apt update
apt install -y fuse-overlayfs
ln -s /usr/bin/fuse-overlayfs /usr/local/bin/fuse-overlayfsInstall Docker Engine on the Linux Container
Since the image I am using is Debian 11, we can follow the official Docker Engine installation instructions for Debian.
Install Docker Engine on Debian
Instructions for installing Docker Engine on Debian
# Ensure pre-requisites are installed
apt install -y ca-certificates curl gnupg lsb-release
# Add Docker GPG key
mkdir -p /etc/apt/keyrings
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/debian/gpg | gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.gpg
# Add Docker apt repository
echo "deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture) signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/docker.gpg] https://download.docker.com/linux/debian $(lsb_release -cs) stable" | tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null
# Update sources and install Docker Engine
apt update
apt install -y docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-compose docker-compose-plugin
# Test for successful installation
docker run hello-world
# Enable the Docker engine to start at boot
systemctl enable dockerReferences
Docker LXC Unprivileged container on Proxmox 7 with ZFS
I’m using Proxmox 7.0-11 on ZFS filesystem and I’m trying to use Dokku (which uses Docker) on a Ubuntu 20.04 LXC Unprivileged container. On the container, I enabled the nesting and keyctl features right after created using the Ubuntu 20.04 template. Here the config: root@srv001:~# pct config…






